volan 15.6 lv | Normal ranges of left ventricular strain: a meta volan 15.6 lv Normal global circumferential strain varied from -20.9% to -27.8% (mean, -23.3%; 95% CI, -24.6% to -22.1%). Global radial strain ranged from 35.1% to 59.0% (mean, 47.3%; 95% CI, 43.6% to 51.0%). There was significant between-study heterogeneity and inconsistency. In November 2001, Christie's auction house sold the original Submariner 5513 from the 1973 James Bond movie "Live and Let Die" for 25,850 GBP (approximately 38,000 USD at the time). The same watch went on the auction block again in 2015, this time at Phillips.
0 · Normal ranges of left ventricular strain: a meta
1 · Global Longitudinal Strain for LV Function
2 · Defining the Reference Range for Left Ventricular Strain in
$12K+
Echocardiographic global longitudinal strain (GLS) has been recommended as .Normal global circumferential strain varied from -20.9% to -27.8% (mean, -23.3%; 95% CI, . This meta-analysis aimed to separately pool the means and LLNs of LV strain . Echocardiographic global longitudinal strain (GLS) has been recommended as a means to follow patients at risk of cancer chemotherapy-related left ventricular (LV) systolic dysfunction. The following are pragmatic points to remember:
Normal ranges of left ventricular strain: a meta
Global Longitudinal Strain for LV Function
Defining the Reference Range for Left Ventricular Strain in
Normal global circumferential strain varied from -20.9% to -27.8% (mean, -23.3%; 95% CI, -24.6% to -22.1%). Global radial strain ranged from 35.1% to 59.0% (mean, 47.3%; 95% CI, 43.6% to 51.0%). There was significant between-study heterogeneity and inconsistency.
This meta-analysis aimed to separately pool the means and LLNs of LV strain measured by MRI from studies of healthy patients and to determine whether patient and MRI factors influence LV strain values.The reference ranges for left ventricular (LV) global longitudinal strain and right ventricular free-wall strain were −24% to −16% and −35% to −17%, respectively. Correspondingly, left atrial (LA) and right atrial (RA) reservoir strains were 17% to 49% and 17% to 59%. Left ventricular (LV) ejection fraction is a routine measure of LV systolic function and has played a critical role in the risk stratification of patients with aortic stenosis (AS). Global longitudinal strain (GLS) <16 percent likely indicates significant myocardial dysfunction, according to results of a meta-analysis presented Aug. 31 at ESC Congress 2019 and simultaneously published in JACC: Cardiovascular Imaging.
LV GLS is useful to detect future cardiotoxicity among patients receiving cardiotoxic chemotherapy, and to detect subclinical LV systolic dysfunction among family members of patients with heritable cardiomyopathies. Several studies have shown that various clinical, ECG, and echocardiographic parameters predict long-term outcome in patients with chronic ischemic cardiomyopathy. 1, 2 In patients with chronic ischemic cardiomyopathy, left ventricular (LV) ejection fraction (EF), and wall motion score index (WMSI) are well-established predictors of long-term ou.
GLS provides a sensitive measure of LV function and appears reduced despite preserved LVEF in several cardiovascular risk conditions, such as advancing age, 3 hypertension, 4 diabetes mellitus, 5 stable angina, 6 renal dysfunction, 7 and obesity. 8 Furthermore, GLS has prognostic value in patients in a range of cardiovascular disorders .Compared with those with a normal LAVI, patients with a severe LAVI had a 42% increased risk of mortality. In patients with normal LV geometry or concentric remodeling, a severe LAVI was a significant independent predictor of mortality, with an increased risk of 28% and 46%, respectively. Echocardiographic global longitudinal strain (GLS) has been recommended as a means to follow patients at risk of cancer chemotherapy-related left ventricular (LV) systolic dysfunction. The following are pragmatic points to remember:Normal global circumferential strain varied from -20.9% to -27.8% (mean, -23.3%; 95% CI, -24.6% to -22.1%). Global radial strain ranged from 35.1% to 59.0% (mean, 47.3%; 95% CI, 43.6% to 51.0%). There was significant between-study heterogeneity and inconsistency.
This meta-analysis aimed to separately pool the means and LLNs of LV strain measured by MRI from studies of healthy patients and to determine whether patient and MRI factors influence LV strain values.The reference ranges for left ventricular (LV) global longitudinal strain and right ventricular free-wall strain were −24% to −16% and −35% to −17%, respectively. Correspondingly, left atrial (LA) and right atrial (RA) reservoir strains were 17% to 49% and 17% to 59%. Left ventricular (LV) ejection fraction is a routine measure of LV systolic function and has played a critical role in the risk stratification of patients with aortic stenosis (AS). Global longitudinal strain (GLS) <16 percent likely indicates significant myocardial dysfunction, according to results of a meta-analysis presented Aug. 31 at ESC Congress 2019 and simultaneously published in JACC: Cardiovascular Imaging.
LV GLS is useful to detect future cardiotoxicity among patients receiving cardiotoxic chemotherapy, and to detect subclinical LV systolic dysfunction among family members of patients with heritable cardiomyopathies. Several studies have shown that various clinical, ECG, and echocardiographic parameters predict long-term outcome in patients with chronic ischemic cardiomyopathy. 1, 2 In patients with chronic ischemic cardiomyopathy, left ventricular (LV) ejection fraction (EF), and wall motion score index (WMSI) are well-established predictors of long-term ou.
GLS provides a sensitive measure of LV function and appears reduced despite preserved LVEF in several cardiovascular risk conditions, such as advancing age, 3 hypertension, 4 diabetes mellitus, 5 stable angina, 6 renal dysfunction, 7 and obesity. 8 Furthermore, GLS has prognostic value in patients in a range of cardiovascular disorders .
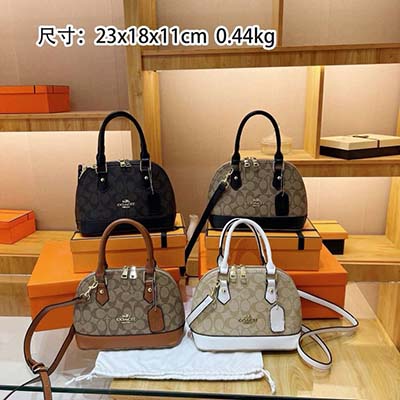
louis vuitton womens wallet replica
replica louis vuitton artsy mm handbag
louis vuitton watch men replica
replica louis vuitton belt aliexpress
$5,094.00
volan 15.6 lv|Normal ranges of left ventricular strain: a meta